Optical Mold Design
– Precision Engineering for Your Optical Needs
As a leading provider of high-precision optical mold design, we serve B2B clients in industries such as automotive, medical, consumer electronics, new energy, and more. Our optical mold design services ensure that your optical components—lenses, prisms, mirrors, and beyond—are manufactured with nanometer-level accuracy, meeting the most demanding performance standards.
What is Optical Mold Design?
Optical mold design is the process of creating molds used to manufacture high-precision optical components, such as lenses, prisms, and mirrors. These components are critical in applications ranging from smartphone cameras and medical imaging systems to automotive sensors and industrial lasers. The quality of the optical mold directly influences the performance of the final component, making precision in design and manufacturing paramount.
Several key factors are considered in optical mold design to ensure the mold meets exact specifications:
- Optical Performance: The mold must produce components that meet precise optical requirements, such as focal length, field of view, and aberration correction.
- Material Compatibility: Selecting appropriate materials for the mold and optical component ensures optimal optical properties and durability.
- Manufacturing Feasibility: The mold design is optimized for the chosen manufacturing process, such as injection molding or glass molding, to enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Optical molds adhere to sub-micron tolerances to ensure the final components meet stringent optical standards.
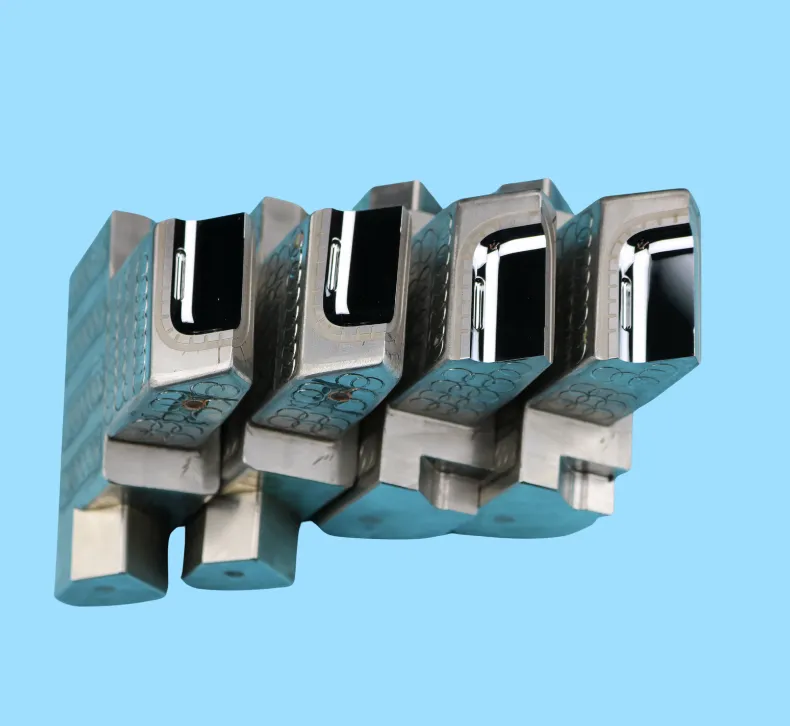


Importance of Precision in Optical Mold Design
The precision of an optical mold directly impacts the quality of the optical component it produces. Even minor deviations, such as surface roughness or dimensional errors, can lead to light transmission losses, aberrations, or reduced system performance. Our optical mold design process addresses these challenges by:
- Achieving surface roughness as low as 2 nanometers (20 Å) for exceptional optical clarity.
- Maintaining dimensional tolerances within ±1 micron for precise component replication.
- Ensuring material stability to withstand high-volume production demands.
By prioritizing precision, we help clients achieve their technical goals while maintaining cost-effectiveness and market competitiveness.
Our Optical Mold Design Process
Yishun Optical follows a comprehensive, client-focused process to ensure every optical mold meets the highest standards of performance, manufacturability, and reliability. Our workflow is designed to deliver customized solutions tailored to your specific needs. Here’s an overview of our five-step process.
Requirement Analysis
We begin by collaborating with you to understand your project’s unique requirements, including:
- Optical specifications, such as focal length, aperture size, field of view, and aberration correction.
- Dimensional tolerances, often requiring sub-micron accuracy.
- Production volume, from prototypes to high-volume manufacturing.
- Material preferences, such as glass, polycarbonate, or cyclic olefin copolymer (COC).
Optical Design
Using industry-leading software like Zemax and Code V, we optimize the optical performance of the component. This stage involves:
- Defining optical properties, including refractive index and dispersion.
- Predicting performance through ray tracing and modulation transfer function (MTF) analysis.
- Minimizing aberrations to ensure high light transmission efficiency.
- Conducting system-level simulations to ensure seamless integration with your optical system.
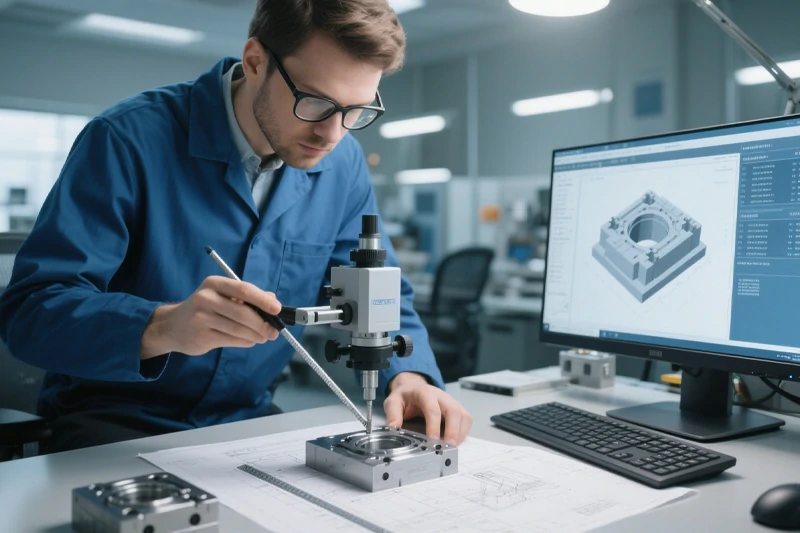
Mold Design
Once the optical design is finalized, we use mechanical CAD software like SolidWorks to create the mold. Key considerations include:
- Configuring the number of cavities, parting lines, and draft angles.
- Designing cooling systems to ensure uniform temperature control and prevent warping.
- Incorporating ejection systems for damage-free part removal.
- Accounting for material shrinkage and thermal expansion to maintain precise dimensions.
Simulation and Validation
Before manufacturing, we perform simulations to validate the mold design:
- Thermal Analysis: Ensures even cooling to prevent defects.
- Structural Analysis: Verifies mold integrity under high-pressure molding conditions.
- Optical Simulation: Predicts the performance of the molded component.
These simulations identify potential issues early, minimizing rework and ensuring reliability.
Prototype and Testing
We create mold prototypes using rapid prototyping techniques and conduct rigorous testing, including:
- Measuring surface roughness with profilometers (e.g., Ra < 10 nm).
- Verifying optical performance with Zygo interferometers to assess wavefront error.
- Checking dimensional accuracy with coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
This ensures the mold meets the highest quality standards before production.
Our process reflects our commitment to precision, collaboration, and quality, delivering optical molds that perform flawlessly.
Technologies and Capabilities
Yishun Optical leverages state-of-the-art technologies and capabilities to deliver superior optical mold design services. Our advanced facilities and skilled team enable us to achieve nanometer-level precision and ensure exceptional quality in every mold.
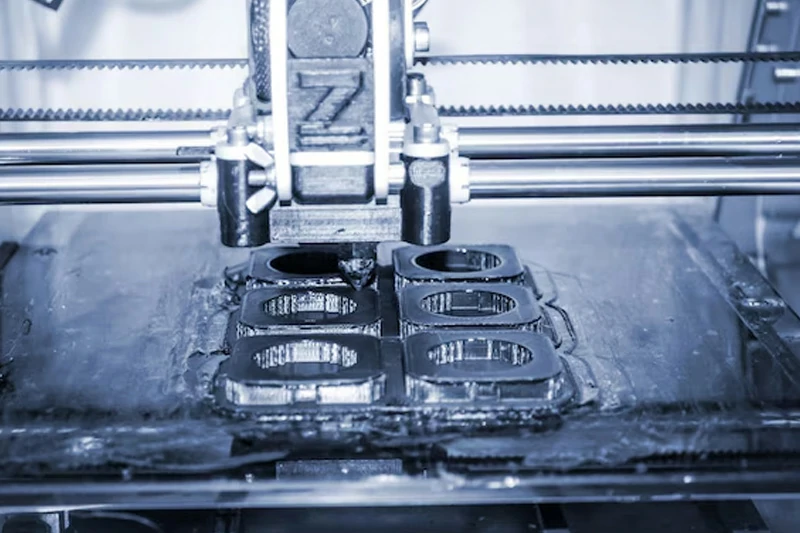

Advanced Technologies
Ultra-Precision Machining:
Single Point Diamond Turning (SPDT) achieves surface finishes as fine as 2 nm, ideal for non-ferrous materials like aluminum and copper.
Ion Beam Figuring (IBF) refines surfaces with sub-nanometer accuracy, ensuring minimal light scattering.
- Injection Molding: Produces plastic optical components with high repeatability and low unit costs.
- Glass Molding: Enables the creation of complex glass optics, such as aspheric lenses, with high precision.
Design Software
- Zemax and Code V for optical performance optimization.
- SolidWorks for precise mechanical mold design.
Quality Control
- Adherence to ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 standards.
- Multiple inspections during design, prototyping, and production to ensure consistency and reliability.
Precision Metrology
- Zygo interferometers measure wavefront error to ensure optical performance.
- Atomic force microscopes (AFM) analyze nanoscale surface topography.
- Coordinate measuring machines (CMM) verify dimensional accuracy within ±1 micron.
Precision Metrology
Category | Materials | Applications |
Mold Materials | Hardened steel, aluminum, ceramics | High-volume production, rapid prototyping |
Optical Materials | Glass, polycarbonate, COC, PMMA, polystyrene | Lenses, prisms, mirrors |
These technologies and materials enable us to deliver optical molds that meet the most stringent industry standards.
Case Studies Rocedure
While client details remain confidential, the following examples highlight our expertise in optical mold design across various industries
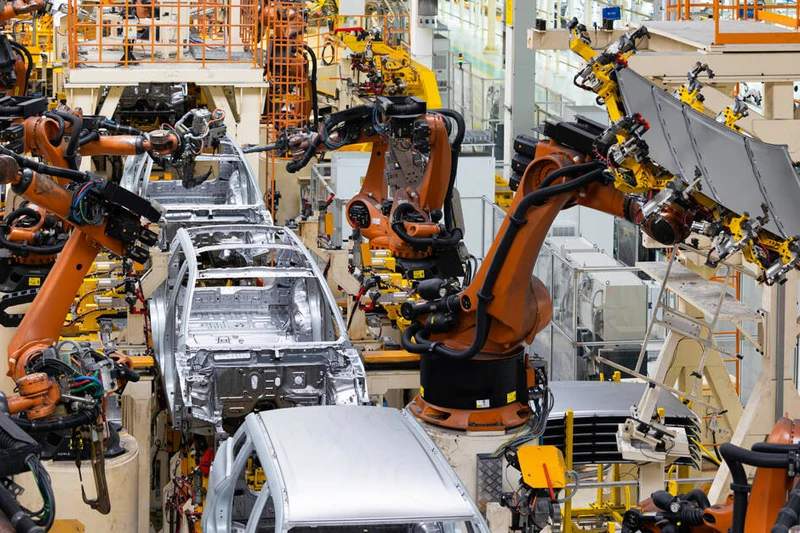

Automotive Industry
- Challenge: Design a mold for camera lenses used in Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) that withstands extreme temperature variations.
- Solution: We selected thermally stable materials and optimized the cooling system to maintain optical performance under harsh conditions.
- Result: The lenses met automotive standards, enhancing ADAS reliability and safety.
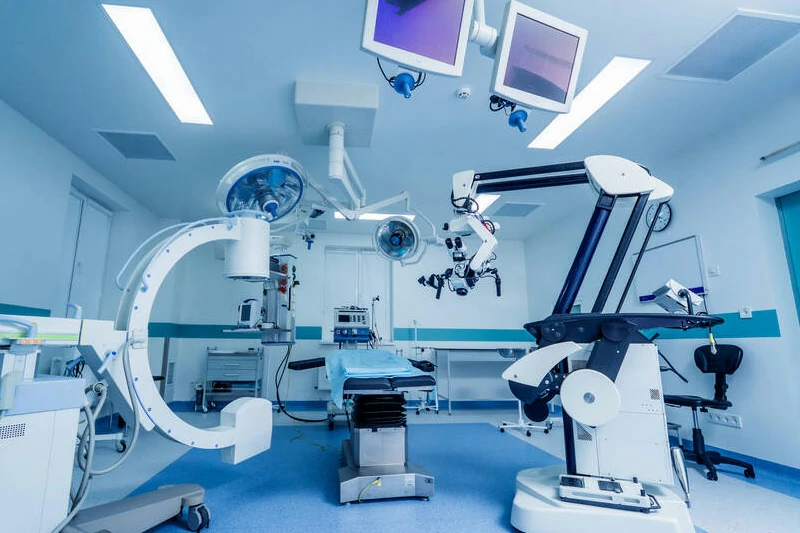
Medical Devices
- Challenge: Develop a mold for aspheric lenses in portable medical imaging devices, requiring compact size and high image quality.
- Solution: Using advanced optical design software, we optimized lens geometry and mold design to reduce size while maintaining performance.
- Result: The device became more portable, improving patient care and diagnostic accuracy.

Consumer Electronics
- Challenge: Mass-produce molds for smartphone camera modules with consistent optical quality across thousands of units.
- Solution: We designed molds with precise surface finishes and tight tolerances, ensuring uniformity.
- Result: The client achieved high production yields, reduced costs, and accelerated market entry.
These case studies demonstrate our ability to deliver customized solutions that address complex challenges and drive client success.
Why Choose Yishun Optical for Optical Mold Design?
Yishun Optical stands out as a premier provider of optical mold design services for several reasons

Unmatched Expertise
Our team of optical engineers and mold designers brings decades of experience, tackling even the most complex projects with confidence.

State-of-the-Art Facilities
Equipped with Class 1000/10000 cleanrooms and advanced metrology tools, we ensure the highest precision in every mold.

Customer-Centric Approach
We collaborate closely with clients from concept to delivery, providing regular updates and incorporating feedback to meet expectations.

Global Reach
Serving clients worldwide, we offer localized support and a deep understanding of regional market needs.
Innovation and Sustainability
We invest in R&D to explore new materials and processes while adopting eco-friendly practices to reduce waste and energy use.
Partnering with Yishun Optical means working with a company that anticipates and addresses future challenges in optical engineering, ensuring your projects succeed.
Get Started with Your Optical Mold Design
Ready to elevate your optical projects with precision-engineered molds? Contact Yishun Optical today to discuss your requirements. Our team is dedicated to providing customized solutions that bring your optical vision to life.
